Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

🔐 Quick Answer: Private local AI offers stronger data control and compliance advantages for real estate and insurance firms
👉 This analysis is for educational purposes. Actual results vary by organization, regulatory context, and implementation quality.
The term “local AI” is often misunderstood in real estate and insurance sectors, where many assume it refers to market-specific AI tools rather than the critical concept of AI systems that operate entirely on-premise to protect sensitive data. This common misconception underplays the urgency of data privacy and compliance challenges these industries face.
Most comparisons overlook the pivotal trade-offs between cloud AI convenience and the legal, financial, and reputational risks resulting from offsite data processing. They fail to address how private local AI solutions uniquely align with HIPAA and GLBA regulations to safeguard client data while enabling advanced AI capabilities.
This article clarifies the true meaning of private local AI, explains its technical implementation tailored for regulated real estate and insurance businesses, and quantifies its ROI by balancing compliance, security, and operational efficiency.
TL;DR Strategic Key Takeaways
Client data leakage has emerged as a critical challenge threatening trust and compliance in the real estate and insurance sectors. As these industries increasingly adopt AI-driven tools, the complexity of safeguarding sensitive information grows, amplifying regulatory and reputational risks.
Understanding the magnitude and nuanced impact of data exposure is essential for decision-makers seeking to balance innovation with stringent privacy mandates like HIPAA and GLBA. This section contextualizes why a privacy-first approach, such as private local AI, is no longer optional but a strategic imperative.
Public cloud AI platforms offer scalability and rapid deployment, but they also introduce complex data governance challenges for real estate and insurance firms handling sensitive client information. When data is transmitted, processed, or stored in third-party environments, organizations must rely heavily on external security controls and contractual safeguards.
Private local AI architectures address many of these governance challenges by keeping sensitive data within controlled infrastructure environments. By processing information on-premise or within isolated private systems, organizations gain greater oversight over how data is accessed, stored, and retained.
| Aspect | Cloud AI | Private Local AI |
|---|---|---|
| Compliance Management | Requires vendor audits, legal reviews, and contractual safeguards | Governed internally through organizational policies |
| Data Exposure Risk | Dependent on third-party infrastructure and network controls | Minimized through localized processing |
| Operational Visibility | Limited insight into backend systems | Full infrastructure and model oversight |
| Cost Structure | Variable, usage-based pricing | Higher upfront cost, predictable operations |
| Client Trust Impact | Requires clear transparency policies | Strengthened by direct data governance |
Understanding these structural differences clarifies why many regulated firms are reassessing their AI deployment models. Private local AI offers a governance-focused approach that aligns operational innovation with long-term compliance and client confidence.
Cloud-based AI platforms combine scalability and rapid deployment with complex governance requirements, particularly when handling sensitive client data in regulated sectors such as real estate and insurance. While technically capable of meeting compliance standards, cloud environments often introduce additional layers of legal, operational, and security oversight.
Industry feedback consistently highlights concerns around data visibility, vendor dependency, and regulatory accountability. Understanding these governance challenges enables organizations to evaluate when private local AI architectures may offer more predictable control and compliance alignment.
Cloud AI services frequently involve transmitting and processing data within third-party infrastructure, requiring firms to rely on external compliance certifications, contractual safeguards, and audit mechanisms. Regulations such as HIPAA and GLBA can be met in cloud environments, but doing so often demands extensive vendor management and documentation.
Multi-tenant architectures, regional data routing, and shared security controls can complicate regulatory verification. Organizations must continuously validate that encryption, access logging, and incident response procedures remain aligned with evolving compliance requirements.
Data security incidents, whether caused by misconfiguration, credential compromise, or third-party exposure, can generate substantial financial and reputational damage. In trust-based industries, even limited breaches may erode client confidence and trigger regulatory scrutiny.
Industry studies estimate that major data incidents frequently result in multi-million-dollar remediation costs, including legal fees, compliance penalties, customer retention programs, and infrastructure upgrades. These indirect costs often exceed immediate technical recovery expenses.
Cloud service dependency can limit organizational flexibility by binding critical AI workloads to external platforms, pricing models, and policy frameworks. Migration between providers or back to internal systems may involve technical, contractual, and compliance-related friction.
Data sovereignty regulations further constrain deployment strategies, as many jurisdictions require sensitive client information to remain within specific geographic or legal boundaries. Managing these obligations across global cloud infrastructures increases compliance complexity.
| Risk Category | Business Impact | Typical Cause | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance Gaps | Regulatory scrutiny, audits, financial penalties | Limited visibility into third-party data handling | Private local AI combined with documented security and audit controls |
| Data Security Incidents | Reputational damage, legal exposure, operational disruption | Misconfiguration, credential compromise, shared infrastructure | Granular access controls, encryption, continuous monitoring |
| Vendor Dependency | Reduced negotiation leverage, rising long-term costs | Proprietary APIs and platform-specific architectures | Hybrid and portable AI deployments using open standards |
| Data Sovereignty Constraints | Regulatory non-compliance, reporting complexity | Cross-border data routing and storage policies | Localized processing and region-specific deployment strategies |
This risk assessment highlights that cloud AI platforms can support regulated workloads when supported by strong governance, contractual safeguards, and continuous oversight. However, these requirements introduce operational complexity and ongoing compliance costs.
For organizations managing highly sensitive client data, private local AI architectures offer a complementary approach by simplifying regulatory alignment, strengthening internal control, and reinforcing long-term client trust.
Clarifying what constitutes private local AI is essential to overcoming common misconceptions found in industry discussions and search results. Unlike cloud-hosted AI platforms, private local AI architectures prioritize on-premise or tightly controlled deployments, ensuring that sensitive client data remains within the organization’s governed infrastructure.
For regulated sectors such as real estate and insurance, this architectural distinction is critical. Meeting compliance obligations under frameworks like HIPAA and GLBA requires demonstrable control over data processing, storage, and access. Properly designed private local AI systems mitigate risks related to data leakage and unauthorized access while maintaining operational efficiency and audit readiness.
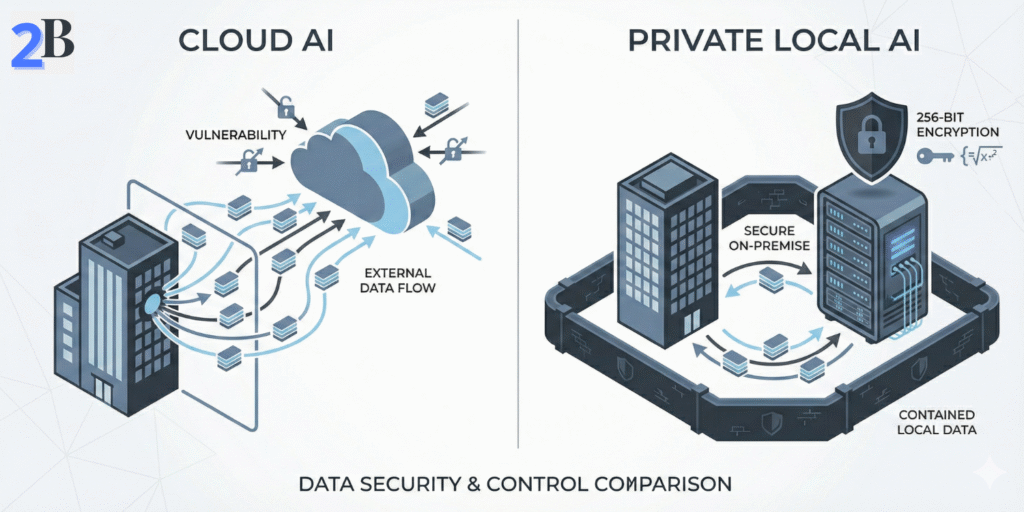
The term local AI is frequently misunderstood as referring to geographically focused AI solutions. In technical and regulatory contexts, however, local AI refers to models and inference systems running inside an organization’s governed infrastructure — either fully on-premise or within tightly controlled private cloud environments.
On-premise and private deployments keep sensitive data, model weights, and inference workloads inside enterprise security boundaries. This architecture reduces external data exposure, simplifies regulatory audits, and strengthens operational accountability. In contrast, public cloud AI platforms typically require data transmission to third-party infrastructure, increasing risks related to data sovereignty, access logging, and compliance verification.
A robust private local AI environment is built on multiple interdependent components designed to preserve confidentiality, integrity, and availability while supporting scalable AI operations:
Adopting open-source AI models and frameworks is a strategic foundation for building sustainable private local AI environments. These technologies enable organizations to retain full visibility and governance over their AI stack while minimizing vendor lock-in and unintended data exposure.
Modern open-source language models, inference engines, and orchestration tools support highly customizable, privacy-oriented deployments for natural language processing, document analysis, and predictive workflows. For regulated industries, this flexibility enables organizations to align AI operations with internal compliance policies and data retention requirements.
| Aspect | Private Local AI (Open-Source Stack) | Cloud-Hosted AI Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Data Governance | Full internal control with defined access, retention, and audit policies | Data managed under provider-specific governance frameworks |
| Compliance Alignment | Easier alignment with HIPAA/GLBA through infrastructure isolation | Dependent on third-party certifications and contractual controls |
| Latency & Reliability | Predictable low-latency inference within internal networks | Variable performance influenced by network and provider load |
| Cost Structure | Capital investment plus predictable operational expenses | Usage-based pricing with long-term scaling risk |
| Customization & Portability | Full control over model tuning, deployment, and migration | Limited by provider APIs and proprietary architectures |
Table 1: Operational and Governance Differences Between Private Local and Cloud-Hosted AI Deployments
By understanding these architectural and governance differences, organizations can design private local AI environments that strengthen compliance, reduce external dependency, and improve long-term operational resilience. In the next section, we will examine how to architect and implement these systems within real estate and insurance infrastructure.
Leveraging private local AI technologies allows real estate and insurance firms to maximize profitability while improving the safeguard of sensitive data. This section examines concrete use cases where local AI delivers measurable ROI by enhancing operational efficiency, client trust, and compliance readiness.
These industry-tailored applications address the dual challenge of extracting actionable insights from proprietary data without risking exposure, a critical factor given stringent regulatory regimes like HIPAA and GLBA. Strategic deployment of on-premise AI empowers firms to meet compliance demands and operationalize AI with confidence.
Real estate firms increasingly leverage private local AI to modernize client acquisition, portfolio management, and operational workflows while maintaining strict data governance. Secure lead scoring systems process historically sensitive inquiry, behavioral, and transaction data within controlled environments, improving targeting accuracy without introducing external data exposure risks.
Private local AI enables firms to develop advanced market intelligence models using granular transaction histories, pricing movements, and internal performance indicators. These datasets, which are often unsuitable for external sharing, support deeper insight into supply-demand imbalances, pricing volatility, and regional investment patterns.
By maintaining analytical workloads within internal infrastructure, organizations preserve competitive intelligence while strengthening auditability and regulatory alignment.
Secure, locally deployed AI-powered communication platforms enable personalized client engagement while processing sensitive inputs entirely within enterprise-controlled systems. This architecture supports advanced recommendation, follow-up, and advisory workflows without routing data through third-party servers.
As a result, firms balance high-touch digital experiences with demonstrable privacy safeguards, reinforcing long-term trust and reducing regulatory exposure.
Insurance carriers increasingly leverage private local AI to automate underwriting, claims assessment, and policy customization while maintaining strict governance over personally identifiable information (PII). Locally deployed models analyze policy histories, behavioral indicators, and documentation within controlled environments, supporting operational efficiency without introducing external data exposure.
Private local AI enables insurers to conduct advanced actuarial modeling and behavioral risk analysis using sensitive datasets isolated from public cloud environments. This architecture supports regulatory alignment, enhances auditability, and reduces exposure to cross-border data transfer risks.
By maintaining internal control over risk pipelines, organizations strengthen governance while preserving analytical depth and decision reliability.
Locally deployed language and vision models enable automated claims analysis without routing sensitive documentation through third-party platforms. This approach improves processing speed and cost efficiency while maintaining complete traceability for regulatory review.
Internalized inference pipelines reduce dependency on external vendors and support consistent enforcement of access, retention, and encryption policies.
| Use Case | Industry | Primary Privacy Focus | Business Impact | Key Technical Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secure Lead Scoring | Real Estate | Internal data processing under governance controls | Higher conversion rates, reduced acquisition costs | Local inference, access segmentation, encrypted storage |
| Private Market Trend Analysis | Real Estate | Protection of proprietary transaction data | Improved investment positioning | High-volume ingestion, model validation, monitoring |
| Automated Policy Underwriting | Insurance | Full internal control of PII and risk data | Faster assessments, operational cost reduction | Compliance-aligned pipelines, governance logging |
| Claims Processing Automation | Insurance | Local handling of sensitive documentation | Accelerated settlements, fraud mitigation | On-premise NLP, audit trails, access management |
Across both real estate and insurance contexts, private local AI enables organizations to balance automation, compliance, and client trust. These deployments reduce operational risk while delivering sustainable efficiency gains supported by transparent governance and infrastructure control.
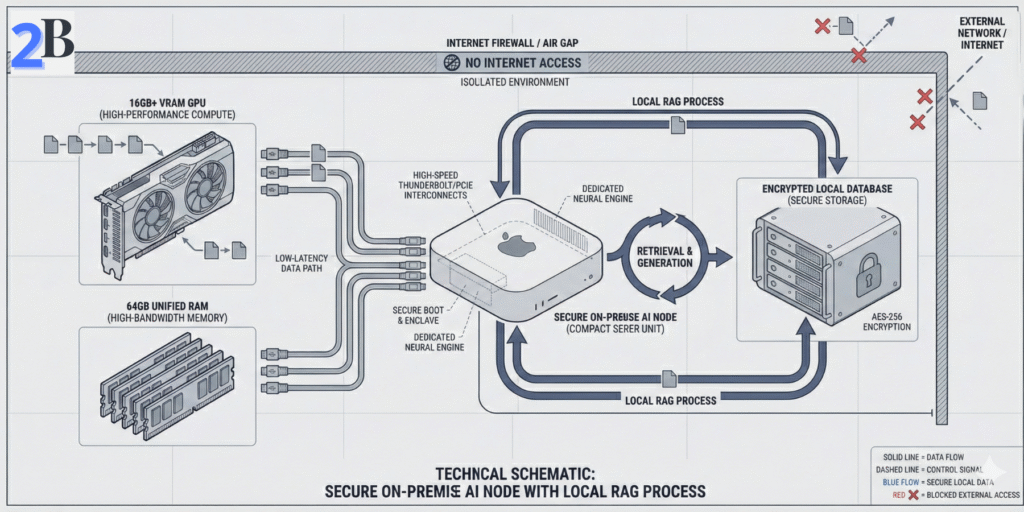
Implementing private local AI requires careful alignment of hardware, software, and governance controls to ensure consistent data protection. To build a resilient system, firms should align their on-premise infrastructure with the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, which provides an industry-recognized baseline for managing operational, security, and compliance risks in generative AI deployments.
Key challenges include selecting compute resources that balance cost and workload demands, choosing an on-premise–optimized software stack, and designing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) architectures that preserve data residency and auditability. Addressing these factors enables measurable risk reduction and sustained control over proprietary client information, supporting long-term HIPAA and GLBA compliance.
Hardware selection fundamentally determines model performance and scalability. For small to mid-sized firms, the Mac Mini M4 has emerged as a high-performance local AI server, offering a cost-effective entry point that balances high unified memory bandwidth with low power consumption.
Deploying private AI locally requires picking software that supports self-hosting and model management. This architecture enables firms to run high-reasoning models like DeepSeek R1 locally with GPT-4 level performance, ensuring that complex document analysis or policy underwriting happens without sending a single byte of data to third-party servers.
RAG architecture combines pretrained LLMs with dedicated local data retrieval systems to generate context-sensitive outputs without exposing private data to the cloud. Properly designed, it enforces strict data locality and enables auditability.
| Component | Key Considerations | Benefits | Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware (GPU vs. CPU) | Compute power, cost, maintenance | Performance scaling, cost-efficiency | GPU higher upfront cost, CPU lower speed |
| Software Stack (LocalAI, Ollama, LM Studio) | Compatibility, extensibility, support | Full control, offline use | Requires in-house expertise, limited cloud benefits |
| RAG Architecture Secure Data Ingestion & Indexing | Data privacy, latency, security | Stronger compliance alignment, contextual accuracy | Complex setup, resource-demanding indexing |
Integrating these components thoughtfully creates a robust, privacy-centric AI environment that aligns tightly with regulatory demands in real estate and insurance, while delivering AI-powered insights without compromising control. The next steps focus on operationalizing data workflows and compliance monitoring.
As businesses in real estate and insurance evaluate AI adoption, understanding the full return on investment (ROI) of private local AI solutions is critical. Beyond upfront costs, ROI includes tangible savings from reduced compliance risks and less visible—yet equally impactful—benefits like enhanced client trust and reputational capital.
Private local AI secures sensitive data on-premise, minimizing exposure to breaches and regulatory penalties. This mitigates costly fines under regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and GLBA (Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act), which can financially dwarf the savings from cloud subscription fees. The challenge is accurately modeling these multifaceted savings to justify upfront investments.
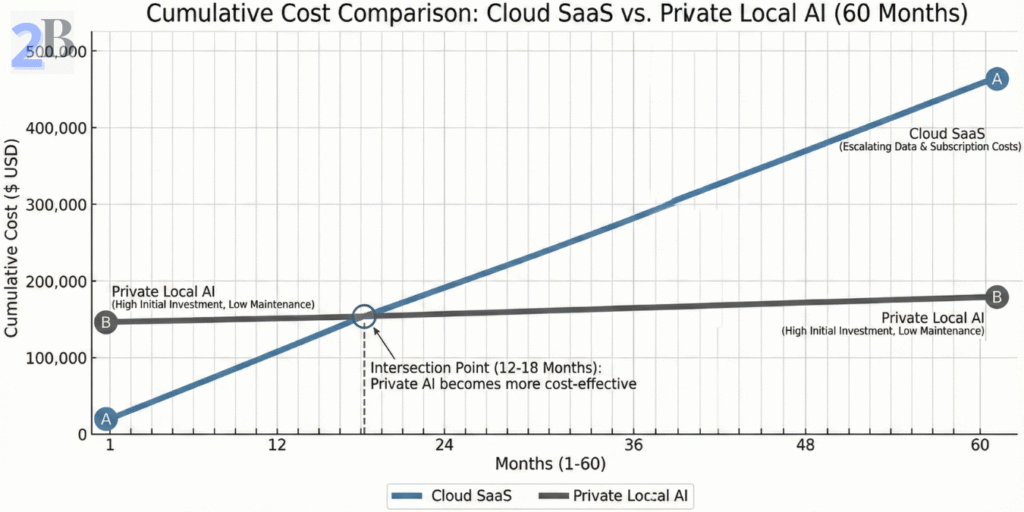
Recurring cloud AI subscription costs accumulate rapidly, especially as data volume and query complexity grow. In contrast, local AI requires an initial infrastructure investment but offers predictable, fixed-cost ownership over time.
Compliance breaches can result in fines ranging from thousands to millions of dollars, damage to business operations, and costly remediation. A risk-adjusted cost-benefit analysis helps quantify how local AI reduces such exposure:
Trust is particularly paramount in real estate and insurance, where clients entrust agencies with highly sensitive personal and financial information. Private local AI boosts confidence by visibly prioritizing data protection, thus fostering loyalty and reducing client churn.
| ROI Component | Benefit | Quantifiable Metric | Trade-offs/Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Cost | Fixed-cost ownership vs. ongoing SaaS fees | Annual depreciation, TCO over 3-5 years | Higher initial capex, requires IT maintenance |
| Compliance & Risk Mitigation | Lower breach probability, audit ease | Cost avoidance from fines, insurance savings | Needs consistent policy enforcement; training costs |
| Client Trust & Reputation | Increased loyalty, higher retention | Reduced churn %, referral rates | Harder to monetize directly; long-term payoff |
When considering AI investments, organizations must evaluate local AI not just by direct costs but by its holistic impact on compliance, risk reduction, and client relationships. Robust financial and business models integrating these factors will ensure more accurate ROI projections and better strategic decisions. Next, we will explore practical deployment frameworks that maximize these advantages within your existing infrastructure.
Understanding when to leverage cloud AI despite the growing appeal of private local AI is critical for realistic, ROI-driven decision-making. This section explores the nuanced trade-offs between control, scalability, and resource allocation that real estate and insurance firms face when choosing AI deployment models.
While private local AI offers robust data privacy and compliance advantages, its operational demands and scaling challenges create scenarios where cloud AI remains the pragmatic option. Evaluating these trade-offs in the specific context of sensitive, regulated data environments ensures aligned technology investments.
Cloud AI platforms excel at handling variable workloads, enabling firms to scale AI capabilities dynamically without upfront infrastructure investment. However, this externalization often entails relinquishing direct control over data processing, which can conflict with HIPAA or GLBA compliance requirements.
Decision-makers must weigh the ability to scale AI services easily against the imperative to maintain data silos under tight control frameworks.
Maintaining private local AI infrastructure demands significant internal expertise in areas such as hardware management, model updating, and security patching. Small to mid-sized firms often struggle with these overheads, making cloud alternatives attractive despite data privacy reservations.
Firms should assess their capacity to build a sustainable internal AI team against long-term costs and compliance risks associated with outsourcing these responsibilities.
Hybrid AI architectures enable firms to retain control over the most sensitive workflows locally while leveraging cloud AI for non-sensitive or high-volume tasks. This model optimizes cost-efficiency and compliance but introduces integration complexity.
Strategic hybrid deployment provides a pragmatic pathway for firms seeking incremental migration without sacrificing either privacy or scale.
| Dimension | Private Local AI | Cloud AI | Hybrid Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Control | Full control; data never leaves premises | Limited control; vendor manages data environment | Control on local sensitive data; cloud for less sensitive |
| Scalability | Limited by local infrastructure; capital-intensive to scale | Highly elastic, pay-as-you-go scaling | Selective scale for cloud tasks; local scales selectively |
| Compliance Complexity | Simplified compliance management internally | Complex due to shared responsibility and vendor audits | Balanced compliance with clear boundary governance |
| Maintenance & Expertise Required | High; requires in-house AI and IT capabilities | Minimal; vendor handles platform management | Moderate; specialized teams maintain local systems and integrations |
| Cost Model | Capital expenditure with ongoing ops cost | Operational expenditure, often subscription-based | Mixed CapEx and OpEx depending on workload split |
Considering the trade-offs outlined here empowers firms to make nuanced, compliance-aligned AI deployment decisions tailored to evolving business and regulatory landscapes. Next, we explore technical strategies to effectively set up private local AI environments optimized for sensitive data workflows.
As AI adoption accelerates in sensitive sectors like real estate and insurance, prioritizing data privacy is non-negotiable. Private local AI emerges as a pivotal approach that balances computational power with airtight compliance, safeguarding client information while delivering scalable business insights.
This model mitigates the critical risks posed by cloud-based AI solutions, notably regulatory non-compliance and data exposure, by processing data on-premise or within secure local environments. Firms gain control over their AI workflows and can embed privacy-by-design principles without sacrificing performance.
Protecting sensitive data must extend beyond traditional IT measures to encompass AI infrastructures. Increasing incidents of cloud data leaks and algorithmic mismanagement highlight compliance gaps under HIPAA, GLBA, and other privacy regulations. Local deployment ensures data remains within a firm’s trusted perimeter, which is crucial for maintaining legal adherence and customer trust.
Integrating private local AI requires a strategic appraisal of your operational needs, compliance mandates, and IT capabilities. Consider these pragmatic evaluation criteria to guide your implementation roadmap:
| Assessment Criteria | Key Questions | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Data Sensitivity | Which data elements are regulated or sensitive? | Determines scope for local processing mandatory for compliance |
| Infrastructure | Do we have sufficient on-premise compute and security controls? | Identifies gaps requiring investment or hybrid cloud strategies |
| Compliance | What regulations impact our AI-driven workflows? | Shapes AI deployment architecture and audit practices |
| Cost & ROI | What savings or revenues arise from increased privacy assurance? | Justifies budget allocation and long-term investment |
| User Adoption | How to ensure seamless transition and employee engagement? | Supports training and change management plans |
Careful alignment of these factors will maximize the strategic advantage private local AI offers, positioning your firm to harness AI innovation while upholding the highest standards of privacy and trust. Consider how this framework applies to evolving your AI infrastructure securely.