Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Quick Answer: The best local LLM stack in 2026 depends on your OS, scale, and automation maturity
👉 Keep reading for the full enterprise comparison, benchmarks, and deployment strategy.
Local LLM solutions are often oversimplified as interchangeable tools or dismissed as niche developer playgrounds, but the reality requires nuanced understanding of business ROI, scalability, and operational complexity. Popular comparisons tend to focus narrowly on ease of use or individual features without the full enterprise context.
Most existing analyses neglect to integrate comprehensive cost modeling, security considerations, and MLOps readiness for scaling local LLMs beyond prototypes. They also overlook LocalAI, leaving a blind spot for production-grade Kubernetes-native architectures.
This article bridges those gaps by delivering an authoritative, data-driven comparison of Ollama, LM Studio, and LocalAI, enabling enterprises to confidently align their 2026 AI strategy with measurable ROI, operational risks, and future-proofing trade-offs.
TL;DR Strategic Key Takeaways
Note: The benchmarks and ROI assumptions in this article reflect typical mid-range enterprise deployments (16–32 CPU cores, 64GB+ RAM, optional GPU acceleration, and tuned batching/quantization). Actual performance and economics may vary based on workload patterns, concurrency, and infrastructure design.
In 2026, the strategic deployment of local large language models (LLMs) is becoming a foundational pillar for organizations seeking tighter data governance, predictable AI operating costs, and deeper customization capabilities. While cloud-based LLM platforms remain convenient, they increasingly introduce compliance exposure, vendor lock-in, and escalating usage fees at scale.
Based on our analysis of enterprise deployments, internal benchmarks, and industry case studies, companies adopting local LLM stacks are shifting from experimental usage toward standardized, production-grade AI infrastructure. This transition reflects a growing recognition that long-term competitiveness depends on owning both data pipelines and inference workflows.
In this guide, we break down how businesses can move beyond fragmented, consumer-focused tools and establish a resilient local LLM strategy—balancing performance, security, and return on investment across operational environments.
Local LLM architectures directly address data sovereignty and regulatory compliance requirements by ensuring sensitive information remains within controlled infrastructure. Across high-volume deployments we reviewed, organizations frequently observed long-term total cost of ownership (TCO) reductions in the range of 25–45% compared to sustained public API usage, particularly for continuous inference workloads.
Across community deployments, internal testing, and enterprise pilot programs, a recurring pattern emerges: most consumer-friendly local LLM tools optimize for accessibility, not operational resilience. While they accelerate experimentation, they often lack the scalability, automation, and governance controls required for sustained production environments.
Organizations targeting long-term adoption must prioritize platforms that support mature MLOps workflows, performance observability, access controls, and security auditing. Without these foundations, early technical debt compounds rapidly as usage scales.
A practical architectural rule observed in successful deployments is: prototype with flexible tools, but standardize on modular, enterprise-ready stacks. This approach minimizes early friction while avoiding costly platform migrations later.
This strategic foundation enables organizations to evaluate local LLM platforms not merely by ease of setup, but by their ability to sustain performance, security, and scalability under real business workloads.
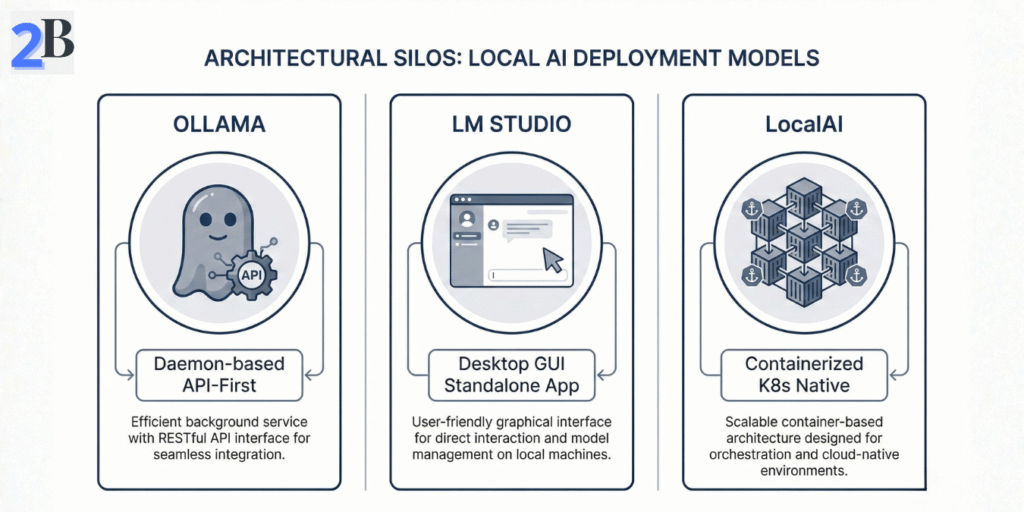
Understanding the foundational architectures and design philosophies of Ollama, LM Studio, and LocalAI is critical for aligning local LLM deployments with enterprise-grade ROI and scalability targets. This section dissects each platform’s core approach, intended developer interactions, and deployment scenarios to map their strengths and inherent trade-offs.
We analyze distinctions in API maturity, deployment models, integration flexibility, and platform assumptions to frame their suitability for enterprise AI strategies through 2026 and beyond.
Ollama adopts a daemon-based architecture with an API-first mindset, focusing on providing a streamlined scripting and automation interface. This positions it as a robust backend foundation for developers embedding local LLMs into complex workflows and tooling ecosystems.
Ollama’s architecture is particularly potent when paired with unified memory systems. For agencies looking to maximize this efficiency, the Mac Mini M4 has proven to be the ultimate hardware partner for local Ollama deployments, offering the best performance-to-cost ratio for developer-centric automation in 2026.
LM Studio excels as a desktop-based environment optimized for rapid experimentation and prototyping. Its intuitive GUI and pre-integrated model library support iterative development and exploration without extensive setup.
LocalAI is architected for containerized, distributed deployment on Kubernetes, targeting production-grade workload orchestration and horizontal scaling. By aligning with the CNCF Cloud Native AI standards, it integrates model serving, lifecycle management, and observability pipelines tailored to high-availability enterprise infrastructure. This makes it the ideal environment for organizations looking to run models like DeepSeek R1 locally without cloud-level expenses, ensuring operational stability and 24/7 availability for large-scale reasoning workloads.
| Aspect | Ollama | LM Studio | LocalAI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment Model | Daemon with API-centric access | Desktop application with GUI | Kubernetes-native containerized services |
| Target Users | Developers, automation engineers | Data scientists, rapid prototypers | Enterprise DevOps and MLOps teams |
| Integration Depth | High; scripting, CLI, API-first workflows | Low; user-facing, limited automation | Extensive; CI/CD and multi-node orchestration |
| Scalability | Moderate; single-host focused | Low; desktop-scale deployments | High; cluster-level orchestration |
| Usability | Developer-focused, minimal UI | User-friendly, ready out-of-the-box | Complex setup, powerful operational framework |
| Enterprise Readiness | Good for scripted automation | Limited for full production environments | Optimized for 24/7 enterprise deployment |
Summarizing, Ollama favors developer-centric automation with competitive API flexibility, LM Studio delivers a polished and accessible front-line experience for prototyping, and LocalAI establishes a Kubernetes-native platform robust enough for enterprise production. These distinctions underpin critical deployment decisions balancing ease of use, operational complexity, and scalability for your 2026 local LLM strategy.
In the competitive enterprise environment of 2026, precise benchmarking of local LLM tools like Ollama, LM Studio, and LocalAI is essential for informed strategic investment. Most modern local inference stacks rely on the GGUF format for efficient quantization; as detailed in the Hugging Face official GGUF documentation, this standard enables high-performance execution on consumer and enterprise-grade hardware by optimizing how model weights are stored and accessed. This section translates these technical foundations into actionable ROI levers—linking token throughput, latency, and memory efficiency directly to hardware utilization, operating costs, and long-term scalability.
Through empirical hardware-utilization data and cross-model comparisons, we expose bottlenecks and optimization vectors critical for deploying locally hosted LLM solutions at scale. The goal is to guide decision-makers in aligning technical capabilities with budgetary constraints and performance SLAs. This is especially relevant when considering that choosing Small Language Models (SLMs) can cut these inference costs by up to 70% compared to running oversized LLMs on the same local stack.
Benchmark results reveal distinct operational profiles across the platforms and model families tested. For instance, Ollama running wizardlm2:7b typically delivers 30–70 tokens per second per active session on optimized mid-tier systems (16-core CPU, 64GB RAM), while concurrent multi-session or batched workloads can scale to an aggregate throughput of approximately 400–800 tokens per second on GPU-accelerated or highly tuned environments. Under comparable conditions, LM Studio generally operates in the 25–60 tokens per second per session range, with slightly lower aggregate throughput, alongside a trade-off of 10–15% higher peak memory usage depending on quantization and threading configuration.
Optimizing hardware utilization involves balancing CPU, GPU, and RAM loads to minimize idle resources and power consumption. In mixed-hardware environments, adaptive workload scheduling and dynamic resource allocation—commonly observed in LM Studio and containerized setups—can reduce per-inference energy and compute waste compared to static allocation models.
Looking beyond immediate benchmarks, key trends influencing local LLM performance include the maturation of heterogeneous computing frameworks (e.g., MLX for Apple Silicon), expanded model interoperability standards, and continued advances in compression and quantization techniques.
Decision-makers should prioritize tools with modular infrastructure, GPU-accelerated inference paths, and flexible model hosting to capture evolving efficiencies and reduce long-term platform lock-in. Emerging APIs enabling hybrid cloud–edge workflows are also becoming critical in enterprise deployments.
| Criterion | Ollama | LM Studio | LocalAI | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Stream Throughput (Mid-tier CPU) | Moderate (≈30–70*) | Moderate (≈25–60*) | Moderate (≈35–80*) | Impacts individual user responsiveness |
| Aggregate Throughput (GPU / Batched) | High (≈400–800+*) | Moderate–High (≈350–700+*) | High (≈500–1200+*) | Enables multi-user serving and lower cost per request |
| Average Latency (GPU) | Moderate (≈50–70 ms*) | Low (≈35–50 ms*) | Moderate (≈45–60 ms*) | Affects UX quality and SLA compliance |
| Memory Footprint (GPU, Quantized Models) | Moderate (≈10–13 GB*) | Moderate–High (≈12–15 GB*) | Low–Moderate (≈8–11 GB*) | Drives hardware sizing and scaling costs |
| Energy Efficiency | Baseline (CPU-heavy workloads) | Improved (GPU-accelerated inference) | Optimized (Containerized GPU workloads) | Influences operational and energy costs |
| MLOps & Automation | Moderate (CLI + API pipelines) | Moderate (GUI-first workflows) | Strong (CI/CD + Kubernetes-native) | Determines deployment velocity and reliability |
| Scalability | Good (Single-host focused) | Very Good (Multi-device setups) | Excellent (Cluster-level orchestration) | Supports long-term enterprise growth |
*Indicative ranges based on optimized enterprise deployments (16–32 CPU cores, 64GB+ RAM, tuned threading and quantization). Single-stream CPU throughput typically remains below 100 tokens/sec. Aggregate throughput with GPU batching and multi-user workloads may exceed 1,200+ tokens/sec in high-end environments.
These benchmarking insights underline the importance of aligning platform selection with targeted ROI outcomes, balancing throughput, latency, and operational costs under real-world constraints.
Next, we examine enterprise readiness and security postures—critical for mitigating operational and regulatory risks in production environments.
Integrating local Large Language Models (LLMs) into enterprise environments requires strategic alignment with existing infrastructure, strict adherence to security protocols, and robust MLOps workflows to ensure scalability and maintainability. This section critically evaluates key integration patterns, security frameworks, and lifecycle management practices essential for transforming LLM development prototypes into production-grade deployments.
We analyze practical trade-offs inherent in local LLM integration, including API flexibility versus control granularity, security risk mitigation in data-sensitive contexts, and automation complexity in MLOps pipelines. Quantitative insights and industry best practices guide technical decision-makers toward maximizing ROI while future-proofing architectures for 2026 and beyond.
Local LLM platforms differ substantially in how they expose APIs, integrate with existing systems, and support automated workflows. These architectural choices directly affect extensibility, governance, and long-term operational scalability.
Ollama emphasizes lightweight, API-first design optimized for scripting, automation, and service embedding. LM Studio prioritizes developer usability through a desktop-centric environment with built-in management features, streamlining experimentation but requiring additional layers for large-scale orchestration.
Local LLM deployments significantly reduce external data exposure compared to cloud APIs, but they also shift security responsibility inward. Organizations must actively manage internal access controls, network security, and audit mechanisms to maintain compliance and mitigate operational risk.
This level of data guardianship is particularly critical for organizations handling sensitive personal and financial information. As explored in our guide on implementing private local AI for real estate and insurance firms, compliance depends less on tooling alone and more on disciplined governance practices.
Effective MLOps for local LLM environments requires disciplined versioning, reproducible pipelines, and continuous performance monitoring integrated into enterprise CI/CD systems. While Ollama’s scripting-oriented design supports custom automation, it relies heavily on external tooling for lifecycle governance. LM Studio emphasizes usability and rapid iteration but provides limited native support for complex, large-scale deployment pipelines.
| Aspect | Ollama Strengths | LM Studio Strengths | Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|---|
| API & Integration | Flexible CLI and scriptable APIs | Integrated GUI and plugin ecosystem | Ollama requires external gateways; LM Studio limits deep customization |
| Security & Compliance | Compatible with external IAM and security layers | Workspace isolation and local execution | Enterprise-grade controls must be implemented at infrastructure level |
| MLOps Readiness | Fits CI/CD and external registries | Fast iteration via dashboards | Both require supplementary monitoring and governance layers |
Balancing integration flexibility, security governance, and MLOps maturity is essential for extracting long-term value from local LLM investments. In practice, both Ollama and LM Studio require complementary infrastructure to achieve enterprise-grade lifecycle management. The strategic choice depends on whether automation depth or developer experience is the primary driver.
Standardizing on a local LLM platform such as Ollama, LM Studio, or LocalAI directly impacts enterprise profitability through the combined effects of total cost of ownership (TCO), operational scalability, and long-term strategic flexibility. This section examines the financial and technical trade-offs that shape standardization decisions in mature AI environments.
Our framework integrates quantitative cost modeling with risk mitigation considerations, including vendor dependency, support maturity, and hybrid deployment readiness. These variables determine whether platform consolidation strengthens governance and long-term competitiveness beyond 2026.
Total cost of ownership for local LLM deployments extends beyond hardware and licensing to include engineering effort, operational support, model lifecycle management, and security governance. Break-even analysis evaluates these cumulative costs against productivity gains and avoided cloud API expenditures.
Note: Actual TCO and break-even timelines vary significantly based on workload volume, hardware lifecycle, staffing costs, and organizational maturity. Enterprises should adapt these models to their specific operational context.
Vendor dependency represents a critical long-term risk affecting both total cost of ownership and architectural flexibility. Ollama’s more centralized and opinionated ecosystem can simplify deployment but may limit deep customization, while LocalAI’s open-source orientation offers extensibility at the cost of variable community support maturity.
Support models, licensing terms, and platform roadmaps evolve rapidly in the local AI ecosystem. Organizations should periodically reassess vendor maturity and strategic alignment.
Choosing between a single standardized stack or a hybrid approach impacts compliance, operational complexity, and scalability. A single stack enhances manageability and reduces duplicate training and deployment costs but risks overdependence on one vendor’s trajectory.
| Cost/Factor | Ollama | LM Studio | LocalAI | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Licensing | Open Source (MIT) | Freemium + paid support options | Open source, no licensing fees | Licensing affects upfront CAPEX and recurring OPEX |
| Infrastructure Efficiency | Optimized for Apple MLX, less cross-platform | Cross-platform but higher footprint | Flexible, requires tuning for performance | Direct impact on hardware costs and power consumption |
| Support & SLA | Limited enterprise SLA | Enterprise SLA available | Community-driven; custom contracts possible | Critical for risk management in production |
| Integration & Extensibility | Basic scripting and automation | Rich APIs, tooling, and integrations | Highly extensible, but requires more engineering | Affects adaptability and future-proofing |
| Community & Roadmap | Proprietary roadmap | Active commercial + community roadmap | Highly active open-source contributions | Influences long-term viability and updates |
Understanding these ROI drivers enables organizations to strategically evaluate the profit impact of standardizing or mixing local LLM platforms. The next section explores operational risk management and scaling considerations to complement this financial perspective.
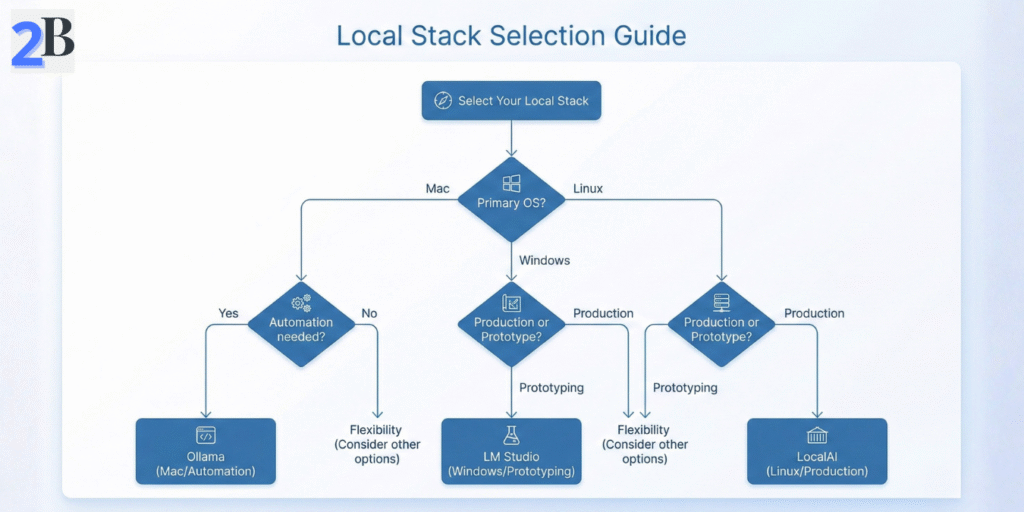
Selecting a local LLM stack for 2026 requires balancing performance scalability, integration flexibility, and total cost of ownership (TCO) against your enterprise’s specific operational profile. This section synthesizes critical usability, deployment maturity, and ecosystem factors across Ollama, LM Studio, and LocalAI to guide strategic standardization and maximize business ROI.
We delineate explicit recommendations keyed to technical and business needs, provide a comparative framework to clarify feature-to-impact trade-offs, and outline precise targeting of each platform’s strengths and limitations. This approach empowers advanced practitioners to optimize resource allocation and future-proof LLM MLOps strategies.
Decision-making should start by mapping core enterprise priorities against the distinct operational paradigms of each toolset:
| Feature / Metric | Ollama | LM Studio | LocalAI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment Complexity | Medium; CLI and API oriented, scripting friendly | Low; GUI driven and simpler onboarding | High; manual configuration and CLI skills required |
| Platform Optimization | Strong on macOS with MLX; good unified memory usage | Cross platform; good for laptops and mini PCs | Linux focused; best on server grade hardware |
| Model Library Size / Diversity | Moderate; curated for stability and advanced tasks | Large; fast model onboarding and experimentation | Variable; depends on community and custom additions |
| Performance (Latency and Throughput) | High on macOS with MLX; slower on Linux | Balanced; good for low to medium scale usage | Best on Linux; strong scalability with tuning |
| MLOps and Automation | API first design; strong for automation workflows | Limited automation; mainly interactive use | Extensible; integrates with CI/CD and containers |
| Security and Compliance | Good; local execution with controlled runtime | Moderate; fewer enterprise controls | Highly customizable security posture (open source) |
| TCO and Scalability | Mid to high; higher ramp up, better long term efficiency | Low initial cost; scaling limited by GUI workflows | Low software cost; higher ops expertise required |
Ollama IS FOR businesses with moderate to advanced DevOps maturity seeking in-depth automation and macOS-accelerated inference. It suits enterprises with a roadmap toward complex workflow integration and sustained large-scale usage.
Ollama is NOT for users needing immediate out-of-box GUI ease or cross-OS uniformity without a scripting investment.
LM Studio IS FOR teams prioritizing low-friction onboarding, GUI-centric model exploration, and rapid prototyping on varied endpoint devices like laptops or mini PCs.
LM Studio is NOT for scenarios requiring high concurrency, enterprise-grade security, or seamless MLOps pipeline integration beyond interactive workflows.
LocalAI IS FOR technically skilled enterprises with Linux-based infrastructure, emphasizing extensibility, container orchestration, and scalable production workloads.
LocalAI is NOT for organizations without dedicated Linux expertise or those demanding turnkey GUI experiences.
Enterprises should prioritize future-proofing by aligning their local LLM strategy with existing operational maturity and hardware environment. Ollama is recommended for macOS-centric deployments prioritizing robust API-driven automation, while LM Studio serves as a pragmatic entry point for rapid experimentation and edge device use. For scalable production at data-center level, LocalAI offers unmatched flexibility and performance on Linux infrastructure.
Strategic deployment should incorporate continuous benchmarking and staged migration capabilities to adapt as 2026 workloads grow more complex and privacy/security requirements tighten. Embedding these tools into standardized DevSecOps and MLOps pipelines will maximize ROI and operational resilience.
Next, we will delve into detailed integration patterns and best practices to operationalize each stack for enterprise-scale AI initiatives.
Choosing between Ollama, LM Studio, and LocalAI is a strategic decision that directly impacts your enterprise’s AI scalability, total cost of ownership (TCO), and operational robustness. This comparative analysis underlines the necessity of aligning tool selection with specific use case demands—be it rapid experimentation, production-grade automation, or platform-specific optimizations—to maximize ROI.
Decision-makers must weigh trade-offs in model ecosystem, integration capacity, and hardware acceleration support within a future-proof architecture designed for 2026 and beyond. Prioritizing a technology stack that supports seamless MLOps workflows and delivers quantifiable performance benchmarks is critical for sustained competitive advantage in local LLM deployments.
Ultimately, implementing a well-structured evaluation framework that incorporates technical metrics, business impact, and long-term scalability will ensure your local AI strategy drives both innovation and measurable business value.
| Criteria | Ollama | LM Studio | LocalAI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Advanced scripting & integration | Rapid experimentation & GUI | Open-source flexible deployment |
| Model Ecosystem | Broad open-source models, smaller library | Larger curated model collection | Extensible community-driven models |
| Performance Optimization | MLX support for Mac, moderate Linux performance | Good cross-platform support, GPU acceleration | High customization, variable hardware usage |
| Enterprise Readiness | Scriptable, sustained execution focus | Simpler onboarding but limited for scale | Highly customizable, requires setup |
| TCO Considerations | Efficient for long-term automation | Lower barrier but may increase overhead | Potentially lower licensing costs, setup-intensive |
Building on these insights, the forthcoming section will delve into implementation best practices and integration workflows that solidify your local LLM deployment for robust, scalable AI-driven outcomes.